Footlogics Orthotics for Children
 Orthotics for young children can be useful when the child displays a flat foot or excessive pronation (fallen arches and rolling inward of the ankle joint). Orthotics can also be useful for young children who experience ongoing aches and pains in the feet or legs, such as:
Orthotics for young children can be useful when the child displays a flat foot or excessive pronation (fallen arches and rolling inward of the ankle joint). Orthotics can also be useful for young children who experience ongoing aches and pains in the feet or legs, such as:
- heel pain (Sever's Disease)
- knee pain (Osgood-Schlatters Disease)
- growing pains
It should be noted that all small children (under 4 years of age) have flat feet and is normal. By the age of 4 to 5 their arches start to develop as the fatty padding under their feet thins. By the age of 7 to 8 a normal arch should be visible.
In a number of children the foot remains flat, or only a very low arch is showing. Arch height is not the main indicator of potential problems. More important is whether your child displays any excess pronation, that is the rolling inward of the ankles and associated low or flat arch.
Excess Pronation
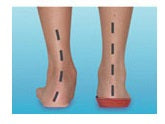
 Excess pronation can be easily identified. If you draw an imaginary line from the tip of the ankle bone downwards to the ground and this line ends away from the foot, your child over pronates and their feet need correcting. Excess pronation may cause an abnormal gait pattern to develop.
Excess pronation can be easily identified. If you draw an imaginary line from the tip of the ankle bone downwards to the ground and this line ends away from the foot, your child over pronates and their feet need correcting. Excess pronation may cause an abnormal gait pattern to develop.
When this happens at a young age children may not experience any specific foot pains or problems, but later on they may be at higher risk of developing conditions.
Such conditions may include:
- children's heel pain (Sever's Disease)
- children's knee pain (Osgood-Schlatters Disease)
- general foot pain
- ankle pain and/or aching legs
Growing pains, which most children will experience to some degree, are often more severe in children with over pronating feet.
Knee pain in Children
Osgood-Schlatters Disease is pain around the front of the knee that commonly occurs in children from the ages of 10 to 15. When the tendon that reaches from the patella (knee cap) to the tibial tuberosity (bump on the front of the shin bone just below the knee cap) pulls excessively. This pulling causes the growth plate located at the tibial tuberosity to become aggravated and inflamed, resulting in pain and discomfort. Overpronation causes the knee to drop inward, thereby increasing the pull of the patella tendon on the tibial tuberosity.
Heel pain in Children
Sever's Disease is a similar condition to Osgood-Schlatters Disease because it also relates to excessive pulling on a growth plate. This condition occurs when the Achilles tendon pulls excessively at its insertion at the back of the heel bone, causing inflammation of the calcaneal apophysis (growth plate). Overpronation contributes to this common complaint because of the increased pull on the Achilles tendon when the foot pronates excessively.
Orthotics for Children
Orthotics can be useful to relieve heel and knee pains in children, as well as many other common foot and leg pains. However if problems persist, consult a Podiatrist.
Recommended Products
Footlogics Kids

